Safari Gets Major Updates with macOS High Sierra Release
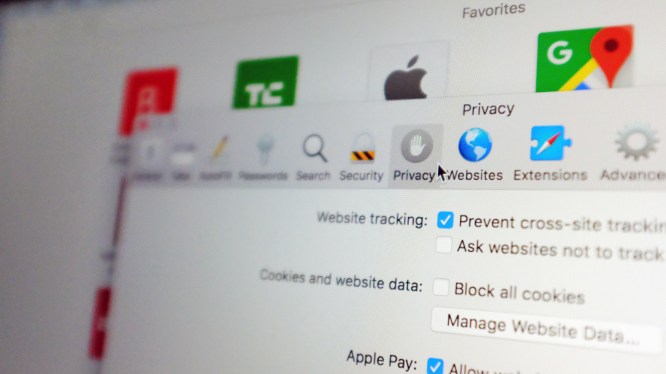
Today marks the public release of macOS High Sierra, which brings with it some significant updates to Apple’s proprietary browser, Safari. One of the most notable additions is the ability for users to disable cross-site cookie tracking and turn off autoplaying ads. These features are sure to please users who value their online privacy.
However, alongside these new features comes a less publicized addition: data collection. Apple has implemented its newly developed differential privacy technology to gather information from user habits. This data will be used to identify problematic websites that use excessive power and crash the browser due to monopolizing too much memory. The company is also documenting the popularity of these domains, allowing it to prioritize which sites it addresses first.
What is Differential Privacy?
Differential privacy is a method for collecting large swaths of information without compromising personally identifying data. This technique, developed from academic research, algorithmically obscures user data while bulk collecting information to identify larger trends. As explained by SVP Craig Federighi in a WWDC keynote, "One of the important tools in making software more intelligent is to spot patterns in how multiple users are using their devices."
Apple has already employed differential privacy for relatively low-level applications, including predictive text in keyboards and emoji usage predictions. This technology is part of the company’s Device Analytics program.
Data Collection with Differential Privacy
The new implementation is already covered by the Device Analytics program that Apple offers when users sign into their new macOS or iOS device. However, more information on this system will be provided in future documentation. Users can choose to participate by ticking an opt-in box, similar to crash reporting. This means that Apple won’t prompt users with additional notifications or sign-up processes for the new data collection.
Benefits and Concerns
The use of differential privacy has given Apple confidence in collecting browsing data without risking the sorts of privacy breaches seen in the past. However, the irony that the company is collecting more browsing data to make its browser more secure won’t be lost on some users. This move highlights the ongoing tension between online security and user privacy.
How Does it Work?
Differential privacy uses complex algorithms to obscure individual user data while aggregating information from multiple sources. This process makes it virtually impossible for Apple or any other entity to trace back any personally identifying information to a specific user.
Implications
The implementation of differential privacy in Safari signals a new approach by Apple in balancing online security with user concerns about data collection. By employing this technology, the company demonstrates its commitment to ensuring users’ online experiences are both secure and private. However, some may question whether collecting more data is truly necessary for improving browser functionality.
Conclusion
The release of macOS High Sierra and Safari’s new features brings about a significant update in Apple’s approach to user data collection. While some users may be concerned about the implications of differential privacy, it’s clear that Apple believes this technology is secure enough to warrant collecting additional browsing data. As always, users have the option to opt-in or out of this feature, providing them with control over their online experience.
Related Topics